上海金畔生物科技有限公司代理New England Biolabs(NEB)酶试剂全线产品,欢迎访问官网了解更多产品信息和订购。
产品信息
Gibson 组装法由 J. Craig Venter 研究所的 Daniel Gibson 博士及其同事发明,由 Synthetic Genomics 公司授权予 NEB 许可。不管片段的长短和末端匹配性如何,该方法都可以成功组装多个 DNA 片段。对于较大的 DNA 构建体而言,该方法易用、灵活、适用性强,因此已被合成生物学领域广泛采用。
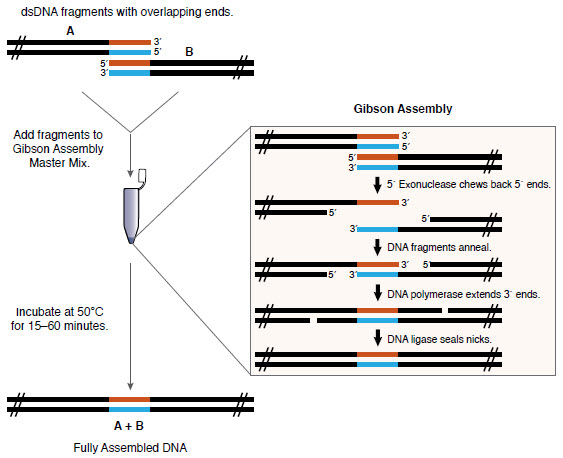
Gibson 组装可在等温条件下,单管反应实现多个带重叠末端的 DNA 片段的组装(1,2)。Gibson 组装预混液在同一反应缓冲液中有三种不同的酶活性:
- 核酸外切酶活性会产生单链 3´ 突出末端,促使互补的末端重复序列(重叠区)退火。
- 聚合酶活性会填补退火片段的缺口。
- DNA 连接酶活性能在组装后的 DNA 切刻处进行连接。
最终形成双链闭合的 DNA 分子,可作为 PCR、RCA 的模板或其它分子生物学应用,包括直接转化。Gibson 的团队和其他研究者们已成功使用该方法组装寡核苷酸、具有多个重叠的 DNA(15–80 bp)以及数百 kb 长的片段(1–2)。
为帮助您选择最佳 DNA 组装方法,请参考合成生物学/DNA 组装选择指南。
如需帮助设计引物,请观看引物设计视频。
Gibson 组装法概述
规格:
10 μl 2X Gibson 组装预混液和 6 个片段(5 个片段为 400 bp,1 个片段为 2,780 bp,重叠为 40 bp,每个 0.05 pmol),在 20 μl 反应体系,50℃ 温育 60 分钟。根据转化操作流程,取 2 μl 预混液/片段混合物转化 NEB 5-alpha E. coli 感受态细胞(NEB #C2987)。在含 IPTG/Xgal 的氨苄青霉素抗性平板上涂布 1/10 的复苏菌液并温育过夜,能观测到 100 个以上白色菌落。
Gibson 组装预混液操作流程概述:
- 设计引物以扩增具有适当重叠的片段(和/或载体)
- 使用超保真 DNA 聚合酶 PCR 扩增片段。
- 使用超保真 DNA 聚合酶通过 PCR 扩增或利用限制性内切酶消化来制备线性化的载体。
- 用琼脂糖凝胶电泳、Nanodrop™ 仪器或其它方法来确定片段浓度
- 将 DNA 添加到 Gibson 组装预混液中,并在 50℃ 温育 15 分钟至 1 小时(时长视组装的片段数量而定)。
- 转化到 E. coli 感受态细胞或直接在其它应用中使用
- 产品类别:
- DNA Assembly, Cloning and Mutagenesis Kits Products
- 应用:
- Gibson Assembly®
-
试剂盒组成
本产品提供以下试剂或组分:
NEB # 名称 组分货号 储存温度 数量 浓度 -
E2611S -20 NEBuilder® Positive Control N2611AVIAL -20 1 x 0.05 ml Not Applicable Gibson Assembly Master Mix M5510AVIAL -20 1 x 0.1 ml 2 X
-
E2611L -20 NEBuilder® Positive Control N2611AVIAL -20 1 x 0.05 ml Not Applicable Gibson Assembly Master Mix M5510AAVIAL -20 1 x 0.5 ml 2 X
-
-
特性和用法
需要但不提供的材料
DNA 聚合酶(用于制备 PCR 产物):
建议使用 Q5® 超保真 DNA 聚合酶(NEB #M0491)或相关产品,例如 Q5 热启动 Flex DNA 聚合酶(NEB #M0493)、Q5 热启动 Flex 2X 预混液(NEB #M0494)。添加了适合的抗生素的 LB(Luria-Bertani)平板。
SOC Outgrowth 培养基(NEB #B9020)。
感受态细胞:
建议使用 NEB 5-alpha E. coli 感受态细胞(高效级,NEB #C2987)。如果是大于 10 kb 的组装产物,NEB 建议使用 NEB 10-beta E. coli 感受态细胞(高效级,NEB #C3019)或 NEB 10-beta E. coli 电转感受态细胞(NEB #C3020)。存储注意事项
- Store at -20°C. Thaw, vortex thoroughly before use and keep on ice.
-
优势和特性
Features
- 增加组装产物的成功率,尤其是组装较大或数量较多的片段
- 灵活的序列设计(无缝克隆)
- 无需纯化步骤
- 一小时内即可完成复杂组装
- 可立即将 DNA 用于转化,或将 DNA 作为 PCR 或 RCA 的模板
- 适用性强,适用于各种 DNA 改造,包括定点突变、插入和缺失
-
相关产品
相关产品
- NEB® 10-beta E. coli 感受态细胞(高效级)
- NEB® 10-beta E. coli 电转感受态细胞
- NEB® 5-alpha E. coli 感受态细胞(高效级)
- SOC Outgrowth 培养基
- Gibson 组装® 克隆试剂盒
- Q5® 热启动超保真 2X 预混液
- Q5® 热启动超保真 DNA 聚合酶
- Q5® 超保真 2X 预混液
- Q5® 超保真 DNA 聚合酶
- t1010-monarch-plasmid-miniprep-kit
- Monarch® DNA 胶回收试剂盒
- Monarch® PCR & DNA 纯化试剂盒(5 μg)
-
注意事项
- 一般说明:
强烈建议使用我们的在线工具 NEBuilder™ 来设计 PCR 引物,使其在相邻 DNA 片段之间具有重叠序列,以将其组装到克隆载体。 - 使用说明:
为确保成功组装以及后续成功转化组装的 DNA,NEB 建议遵循以下做法:
- 细胞:感受态细胞的转化效率可能相差几个数量级。观察到的组装效率与用于转化的感受态细胞效率直接相关。
- 电转化:电转化可以将转化效率提高几个数量级。将 Gibson 组装预混液产品用于电转化时,需要将反应液稀释 3 倍,并取 1 μl 用于转化。
- DNA:如果 Gibson 组装反应液中所有 PCR 产物的总体积不超过 Gibson 组装反应体积的 20%,无需进行 PCR 产物纯化。PCR 产物体积过多会引入更多 PCR 产物中存在的 PCR 反应缓冲液和未使用的引物,从而降低 Gibson 组装和转化的效率。PCR 产物柱纯化可能会使 Gibson 组装和转化的效率增加 2 – 10 倍,在组装三个或更多 PCR 片段时,或组装长度超过 5 kb 的片段时,强烈建议进行 PCR 产物柱纯化。用于组装的纯化 DNA 可溶于 ddH2O(推荐使用 Milli-Q® 水或同等纯度的水)、TE 或其它稀释缓冲液。
- 插入片段:直接将片段组装到克隆载体中时,组装片段的浓度应比载体浓度高至少 2–3 倍。组装三个或更多片段时,建议使用等摩尔比的片段。
- 生物学特性:一些 DNA 结构,包括反向重复序列和串联重复序列,会被大肠杆菌选择性丢失。大肠杆菌无法耐受某些重组蛋白,因此可能会导致转化效率较低或菌落较小。
- 一般说明:
-
参考文献
- Gibson, D.G. et.al (2009). NatureMethods. 343-345.
- Gibson, D.G. et al. (2010). NatureMethods. 901-903.
- Barnes, W.M. (1994). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci.. 91, 2216-2220.
操作说明、说明书 & 用法
-
操作说明
- Gibson Assembly® Master Mix – Assembly (E2611)
- Gibson Assembly® Chemical Transformation Protocol (E2611)
- Gibson Assembly® Electrocompetent Cells Transformation Protocol (E2611)
-
说明书
产品说明书包含产品使用的详细信息、产品配方和质控分析。- manualE2611_E5510
-
应用实例
- Improved methods for site-directed mutagenesis using Gibson Assembly® Master Mix
工具 & 资源
-
选择指南
- Synthetic Biology/DNA Assembly Selection Chart
-
Web 工具
- NEBuilder® Assembly Tool
FAQs & 问题解决指南
-
FAQs
- I am not sure whether to choose NEBuilder HiFi DNA Assembly or NEB Gibson Assembly? How are the products different?
- What are the advantages of this method compared to traditional cloning methods?
- How large a DNA fragment can I assemble?
- How many fragments of DNA can be assembled in one reaction?
- What are the shortest overlaps that can be used with this assembly method?
- What are the longest overlaps that can be used with this method?
- Can ≤ 200 bp dsDNA fragments be assembled by this method?
- Can ssDNA oligonucleotides be combined and assembled with dsDNA fragments?
- Can longer or shorter incubation times be used?
- Will the reaction work at other temperatures?
- Is it necessary to inactivate restriction enzymes after vector digestion?
- I would like to produce overlapping dsDNA fragments by PCR. Do I need to use PCR primers that have been purified by PAGE or HPLC?
- I would like to assemble ssDNA oligonucleotides into dsDNA fragments. Do I need to use oligonucleotides that have been purified by PAGE or HPLC?
- Can I use a 15-nt overlap that is entirely composed of His-tag repeats (i.e. CACCACCACCACCAC)?
- Can you PCR-amplify the assembled product?
- What should I do if my assembly reaction yields no colonies, a small number of colonies, or clones with the incorrect insert size following transformation into E. coli?
- How can I reduce the number of vector-only background colonies?
- What type of competent cells are suitable for transformation of DNA constructs created using Gibson Assembly?
- Can I use electroporation instead of chemical transformation?
- Are there any differences between the Gibson Assembly Master Mix (NEB #E2611) and Gibson Assembly Master Mix included in the Gibson Assembly Cloning Kit (NEB #E5510)?
- Are there any differences between the requirements for 2-3 fragmentassemblies versus 4–6?
- The Gibson Assembly Master Mix control reaction is not giving me any colonies. Why?
- When using a polymerase that doesn’t contain a 3′-5′ exonuclease activity (such as Taq DNA Polymerase) to amplify fragments to be used in a Gibson Assembly reaction, should I be concerned about the potential 3′ mismatch generated by the addition of a non-templated nucleotide?
- Is storing Gibson Assembly Master Mix at -80°C harmful?
- I would like to use NEBuilder but am concerned about user data privacy. How does NEB handle the information that I enter into NEBuilder?
- Can I Use other primer design tools such as SnapGene for Gibson Assembly, to design primers for NEBuilder HiFi DNA Assembly?
- What antibiotic resistance is encoded in the NEBuilder Positive Control (assembly control)?

